Blind Spot Monitors Explained for Students in Automotive Schools
Blind spot monitors aren’t just cool features— they can save lives, too. When a blind spot monitor is installed in a vehicle, the driver can view cars to their rear and sides that may be getting too close for comfort.
How blind spot monitors work depends on the vehicle, but each one helps drivers see potential hazards they otherwise might not have seen.
While they are typically optional, there are many reasons to believe they’re worth the extra money. Here’s what automotive school students need to know about blind spot monitors.
How Do Blind Spot Monitors Work?
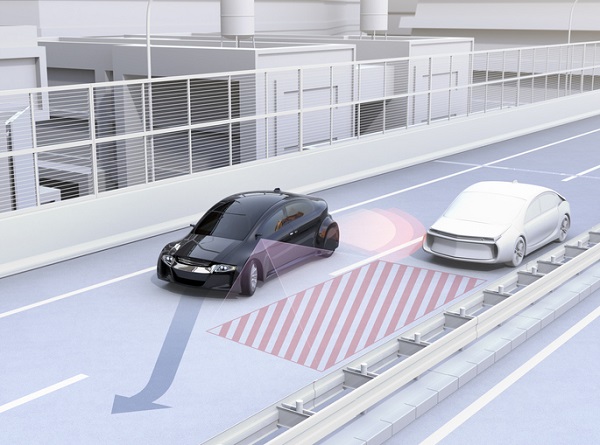
While a car is in use, the blind spot monitor oversees the lanes on their left and their right, particularly spots over the driver’s shoulder that they may otherwise have difficulty seeing.
The system is often comprised of two major parts: the indicator (many of which come equipped with both alarms and LED lights), and the sensor, which sets the indicator off upon examining the environment in front of it.
These systems typically operate at speeds higher than 32 to 56 km/h, and some systems will be able to detect vehicles that are several cars behind the driver, rather than directly near them.
The systems alert the driver when a car is in their blind spot, often by activating a light on the vehicle’s outside door mirror. In most cases, this is all that it really needs to do, although the monitor will also send alerts to the driver if they try turning on their signal to make a lane change while a car is in their blind spot. This can either be done with a noise such as a chime, or with a flashing light. Some more advanced systems can even have the vehicle steer itself back into safety.

Students at automotive schools should also know that some cars can be equipped with cameras to show the driver large, detailed images of what’s in their blind spot.
The Tech Behind Blind Spot Monitors Explained for Students in Automotive Schools
One of the benefits of having a blind spot monitor is that it makes driving conditions safer, mainly through making the blind spotless of a hazard for drivers. While the monitoring systems of each car manufacturer will vary, the technology is often grouped into either active or passive monitoring.
With active monitoring, the system uses a detection device on the car’s sides, either capturing images or sending electromagnetic waves to notify the driver about oncoming vehicles. Passive monitoring systems have a special mirror installed in the corner of the driver’s external rearview mirror to see areas typical rearview mirrors don’t.

Recommending Blind Spot Monitors to Customers During Your Auto Mechanic Career
Although factory-installed blind spot monitoring systems are mostly found in luxury vehicles right now, they are expected to become more affordable for ordinary drivers within the next few years.
Furthermore, they are considered a smart investment as an aftermarket purchase for those who drive older vehicles where such safety features are nonexistent. Graduates of auto mechanic courses would do well to recommend them to any driver who wants to be more aware of their surroundings and enjoy a safer ride.
Interested in an auto mechanic career in Cambridge?
Contact Automotive Training Centres for more information!

